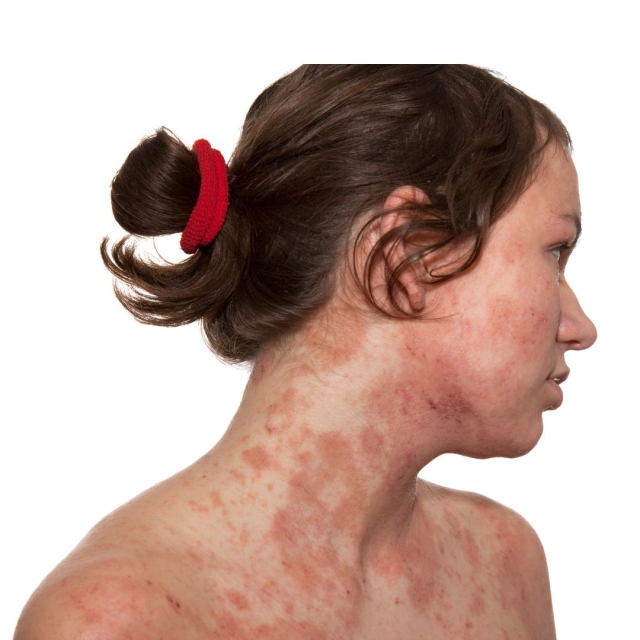
Dermatitis is an inflammatory skin condition that can cause redness, swelling, and itching. It is a common condition that affects people of all ages, from babies to older adults. There are different types of dermatitis, each with its own causes and treatments.
Types of Dermatitis
There are several types of dermatitis, each with specific characteristics and causes:
Atopic Dermatitis: Also known as eczema, it is a chronic condition that usually begins in childhood. It is characterized by dry, itchy skin, and may be associated with other allergic conditions such as asthma and allergic rhinitis.
Contact Dermatitis: This occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritating or allergic substance. There are two main types: irritant contact dermatitis, caused by substances that damage the skin's protective layer, and allergic contact dermatitis, which is an allergic reaction to a specific substance.
Seborrheic Dermatitis: It mainly affects the scalp and manifests itself as dandruff or yellowish scabs. It can also affect other oily areas of the body such as the face, chest, and back.
Numular Dermatitis: It presents as round, well-defined spots on the skin. It can be caused by dry skin, and is often exacerbated in winter.
Stasis Dermatitis: Occurs in people with poor circulation in the legs. The skin becomes reddish and may be swollen and itchy. It is common in people with varicose veins.
Symptoms of Dermatitis
Dermatitis symptoms can vary depending on the type, but some common signs include:
Skin redness: Inflammation causes redness and may be accompanied by swelling.
Itching : It is one of the most annoying symptoms, and scratching can worsen the condition.
Dryness and peeling : The affected skin may become very dry and peel.
Blisters and scabs: In severe cases, blisters may appear that ooze and form scabs.
Thickening of the skin: The skin can become thick and leathery over time, especially if the dermatitis is chronic and not treated properly.
Causes of Dermatitis
The causes of dermatitis vary depending on the type:
Genetics : Atopic dermatitis, for example, is often found in families with a history of allergies.
Irritant substances or allergens: Chemicals, cosmetics, detergents and certain metals can trigger contact dermatitis.
Poor health conditions: Seborrheic dermatitis is associated with conditions such as HIV and Parkinson's disease.
Circulation problems: Stasis dermatitis is caused by circulation problems in the legs.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of dermatitis is usually made through a physical examination and review of the patient's medical history. In some cases, additional tests may be needed:
Patch tests: Used to identify substances that cause allergic contact dermatitis.
Skin biopsy: In cases where the diagnosis is unclear, a skin sample can be taken for analysis.
Allergy testing: To determine if an allergy is the underlying cause.
Treatment
Dermatitis treatment depends on the type and severity of the condition:
Topical Medications: Creams and ointments containing corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and itching. Calcineurin inhibitors, such as tacrolimus, may also be effective.
Antihistamines: These medications can help reduce itching, especially at night.
Antibiotics : If the skin becomes infected, topical or oral antibiotics may be necessary.
Moisturizers : Keeping the skin hydrated is crucial for managing dermatitis, especially in the case of atopic dermatitis.
Phototherapy : Controlled exposure to ultraviolet light may be beneficial for some types of dermatitis.
Management and Prevention
Management of dermatitis includes both medical treatment and lifestyle changes to avoid triggers:
Avoid triggers: Identifying and avoiding substances that cause reactions is crucial to preventing flares.
Skin care: Using mild soaps, avoiding long hot baths, and applying moisturizers regularly can help keep skin healthy.
Appropriate clothing : Wear cotton clothing and avoid irritating materials such as wool.
Controlled environment: Keeping the home free of dust and other allergens can help reduce symptoms.
Nutrition : A balanced diet and avoiding foods that may cause allergies is also important.
Complications
If not treated properly, dermatitis can lead to serious complications:
Infections : Damaged skin is more susceptible to bacterial, viral and fungal infections.
Sleep problems : Severe itching can interfere with sleep, affecting quality of life.
Psychological problems : Chronic dermatitis can affect self-esteem and lead to anxiety and depression problems.
Dermatitis is a common condition but manageable with proper care and medical attention. Identifying the specific type of dermatitis and understanding its causes and triggers is crucial for effective management. With proper treatment and lifestyle changes, people with dermatitis can live comfortably and reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.